- 9 de Março de 2026 - Segunda
PNEUMOMEDIASTINO
Complicações da asmaPESQUISA DE IMAGENS
- ABSCESSO PULMONAR
- ANATOMIA RADIOLÓGICA
- ASMA
- BRONQUIECTASIAS
- BRONQUIOLITES
- DIVERSOS
- DOENÇA DO REFLUXO GASTRESOFÁGICO
- DOENÇAS FÚNGICAS
- DOENÇAS INTERSTICIAIS
- DOENÇAS OCUPACIONAIS
- DOENÇAS PLEURAIS
- DOENÇAS VASCULARES
- DPOC
- METÁSTASES
- MICOBACTERIOSES NÃO-TUBERCULOSAS
- NEOPLASIAS
- NÓDULOS
- OUTROS ÓRGÃOS
- PNEUMONIAS
- TUBERCULOSE
- VIAS AÉREAS SUPERIORES
PNEUMOMEDIASTINO

Observe a presença de ar deslocando lateralmente a pleura mediastinal (setas brancas), dando a impressão de uma linha que contorna o coração, caracterizando o pneumomediastino. As setas amarelas apontam para o ar no tecido subcutâneo, caracterizando o enfisema subcutâneo.
O pneumomediastino espontâneo foi descrito pela primeira vez por Hamman (1939) e é uma complicação rara na asma. Caracteriza-se pela presença de ar no mediastino.
*****
Note the presence of air laterally displacing the mediastinal pleura (white arrows), as a line that surrounds the heart, characteristic of pneumomediastinum. The yellow arrows point to the air in the subcutaneous tissue, featuring the subcutaneous emphysema.
Spontaneous pneumomediastinum was first described by Hamman (1939) and is a rare complication in asthma. It is characterized by the presence of air in the mediastinum.
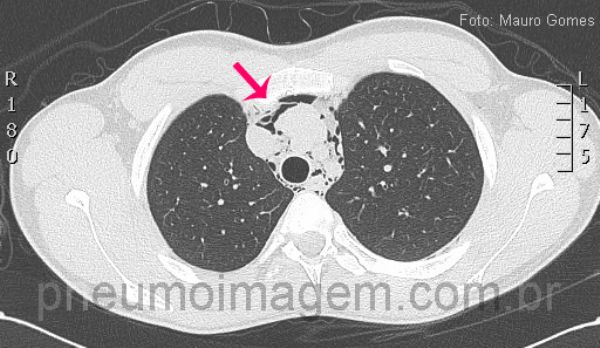
Corte tomográfico ao nível da traquéia demonstra a presença de ar dissecando as estruturas mediastinais e vasculares (seta vermelha). No pneumomediastino espontâneo não há evidências de traumatismo, iatrogenia ou pneumopatias prévias. Por se tratar de uma afecção incomum, eventualmente o diagnóstico não é feito, o que pode trazer consequências danosas e até mesmo fatais para o paciente.
*****
CT slice at the level of the trachea demonstrating the presence of air dissecting mediastinal and vascular structures (red arrows). In spontaneous pneumomediastinum there is no evidence of trauma, iatrogenic or prior pulmonary diseases. It is an uncommon condition and diagnosis can be delayed and may have consequences harmful and even fatal to the patient.
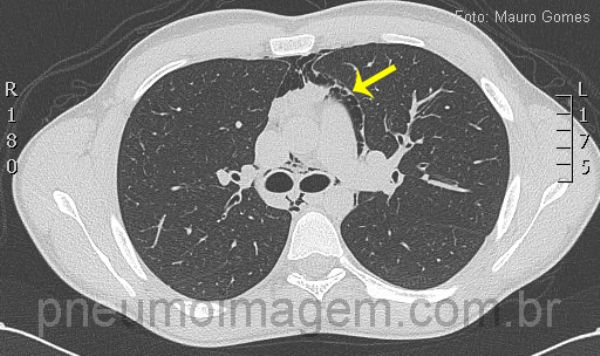
Corte tomográfico ao nível da carina demonstra a presença de ar dissecando as estruturas mediastinais, vasculares e brônquios. Observe a pleura deslocada da aorta devido à interposição de ar (seta). O pneumomediastino pode ocasionar dor torácica com irradiação para o pescoço, dispneia e enfisema subcutâneo, sendo uma rara complicação da asma.
*****
CT slice at the level of the carina demonstrating the presence of air dissecting mediastinal, vascular and bronchial strucutures. Look at the pleura displaced of the aorta due to the interposition of air (arrow). Pneumomediastinum can cause chest pain irradiating to the neck, dyspnea and subcutaneous emphysema, being a rare complication of asthma.
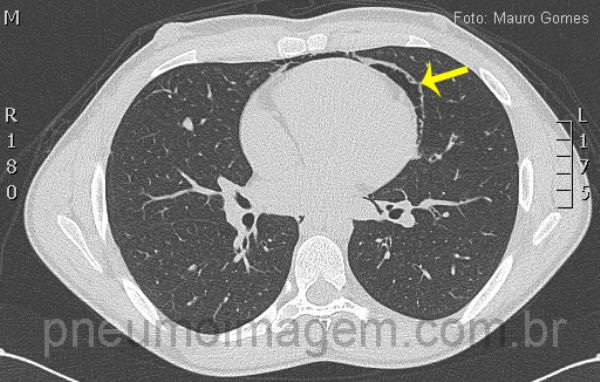
Neste corte observa-se o ar deslocando a pleura mediastinal e formando uma linha que circunda o coração (seta). Este é um jovem paciente do sexo masculino, com 19 anos, que sentiu dor torácica e dispneia durante uma partida de futebol.
*****
In this section we observe the air displacing mediastinal pleura and shaping a line that surrounds the heart (arrow).
This is a young male patient, aged 19, he felt chest pain and dyspnoea during a soccer match.



1 COMENTÁRIOS
Jorge E. Manhães de Carvalho
Pneumologia
Niterói - RJ - 30/10/2013 17:13DEIXE SEU COMENTÁRIO