- 14 de Março de 2026 - Sábado
LINFANGIOLEIOMIOMATOSE
Doenças Císticas PulmonaresPESQUISA DE IMAGENS
- ABSCESSO PULMONAR
- ANATOMIA RADIOLÓGICA
- ASMA
- BRONQUIECTASIAS
- BRONQUIOLITES
- DIVERSOS
- DOENÇA DO REFLUXO GASTRESOFÁGICO
- DOENÇAS FÚNGICAS
- DOENÇAS INTERSTICIAIS
- DOENÇAS OCUPACIONAIS
- DOENÇAS PLEURAIS
- DOENÇAS VASCULARES
- DPOC
- METÁSTASES
- MICOBACTERIOSES NÃO-TUBERCULOSAS
- NEOPLASIAS
- NÓDULOS
- OUTROS ÓRGÃOS
- PNEUMONIAS
- TUBERCULOSE
- VIAS AÉREAS SUPERIORES
LINFANGIOLEIOMIOMATOSE

A Linfangioleiomiomatose (LAM) resulta da hiperproliferação anormal de células de músculo liso nos pulmões, associada com a formação de cistos parenquimatosos difusos e dispneia. As imagens radiológicas correspondem a opacidades intersticiais e pequenos cistos difusos bilateralmente.
A doença atinge preferencialmente mulheres e complica com pneumotórax e derrame pleural quiloso. O transplante pulmonar permanece como o único tratamento válido. Estudo apontou que as células da LAM expressam marcadores associados com diferenciação melanocítica, sugerindo que terapêuticas vacinais dirigidas a esses alvos podem ter sucesso no tratamento da doença (Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. January 1, 2012 vol. 46 no. 1 1-5 ).
*****
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) results from the abnormal hyperproliferation of smooth muscle cells in the lungs, associated with the formation of diffuse parenchymal cysts and dyspnea. The radiological images correspond to interstitial opacities and bilaterally diffuse small cysts.
The disease predominantly affects women and complicates with pneumothorax and chylous pleural effusion. Pulmonary transplantation remains the only valid treatment. A study indicated that LAM cells express markers associated with melanocytic differentiation, suggesting that vaccine therapies targeting these targets may be successful in treating the disease (Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. January 1, 2012 vol. 46 no. 1 1-5 ).
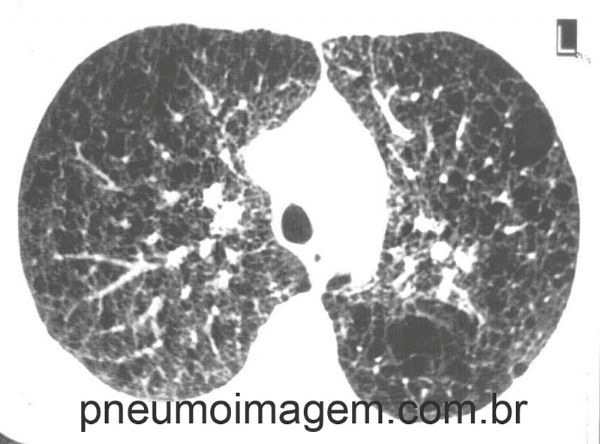
Corte tomográfico em LAM demonstrando cistos de paredes finas com distribuição difusa. Espessamento septal e opacidades em vidro fosco. Pequenos nódulos.
*****
CT scanning in LAM demonstrating thin-walled cysts with diffuse distribution. Septal thickening and ground glass opacities. Small nodules.



DEIXE SEU COMENTÁRIO